Description
STANDARD TYPES OF FLANGES
WELDING NECK FLANGE
 .
. 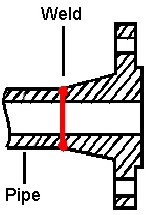 A welding neck flange (“WN”)features a long tapered hub that can be welded with a pipe. This flange type is used, normally, in high-pressure and high/low temperatures applications that require an unrestricted flow of the fluid conveyed by the piping system (the bore of the flange matches with the bore of the pipe). The absence of pressure drops prevents negative effects as turbulence and erosion/corrosion of the metals in the proximity of the flanged joints. The tapered hub allows a smooth distribution of the mechanical stress between the pipe and the weld neck flange and facilitates the execution of radiographic inspections to detect possible leakages and welding defects. The dimension of the flange (NPS and the pipe schedule) shall match the dimension of the connecting pipe. A welding neck flange is connected to a pipe by a single full penetration V-shaped butt weld.
A welding neck flange (“WN”)features a long tapered hub that can be welded with a pipe. This flange type is used, normally, in high-pressure and high/low temperatures applications that require an unrestricted flow of the fluid conveyed by the piping system (the bore of the flange matches with the bore of the pipe). The absence of pressure drops prevents negative effects as turbulence and erosion/corrosion of the metals in the proximity of the flanged joints. The tapered hub allows a smooth distribution of the mechanical stress between the pipe and the weld neck flange and facilitates the execution of radiographic inspections to detect possible leakages and welding defects. The dimension of the flange (NPS and the pipe schedule) shall match the dimension of the connecting pipe. A welding neck flange is connected to a pipe by a single full penetration V-shaped butt weld.
LONG WELDING NECK
 Long weld neck flanges (“LWN”) are similar to weld neck flanges, with the exception that the neck (tapered hub) is extended and acts like a boring extension.
Long weld neck flanges (“LWN”) are similar to weld neck flanges, with the exception that the neck (tapered hub) is extended and acts like a boring extension.
SLIP ON FLANGE

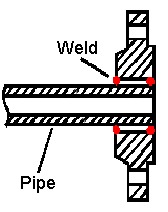 A slip-on flange is connected to the pipe or the fittings by two fillet welds, one executed inside and one outside the cavity of the flange. The bore size of a slip-on flange is larger than the outside diameter of the connecting pipe, as the pipe has to slide inside the flange to be connected by the execution of a fillet weld. Slip-on flanges are also defined “Hubbed Flanges” and they are easy to recognize due to their slim and compact shape. The dimensions and weights of slip-on flanges ANSI/ASME are available on this page. WELD NECK VS SLIP ON FLANGE Flanged joints made with slip-on flanges are, in the long run, a bit more fragile than connections made with welding neck flanges (in similar service conditions). This seems due to the following facts:
A slip-on flange is connected to the pipe or the fittings by two fillet welds, one executed inside and one outside the cavity of the flange. The bore size of a slip-on flange is larger than the outside diameter of the connecting pipe, as the pipe has to slide inside the flange to be connected by the execution of a fillet weld. Slip-on flanges are also defined “Hubbed Flanges” and they are easy to recognize due to their slim and compact shape. The dimensions and weights of slip-on flanges ANSI/ASME are available on this page. WELD NECK VS SLIP ON FLANGE Flanged joints made with slip-on flanges are, in the long run, a bit more fragile than connections made with welding neck flanges (in similar service conditions). This seems due to the following facts:
- a welding neck flange features a tapered hub, absent in a socket weld flange, which distributes the mechanical stress between the pipe and the flange more evenly
- a welding neck joint as only one welding area instead of two (socket weld flange).
Another advantage of the welding neck flange is that it can be connected either to pipes and fittings, whereas socket weld flanges suit pipes only.
THREADED FLANGE

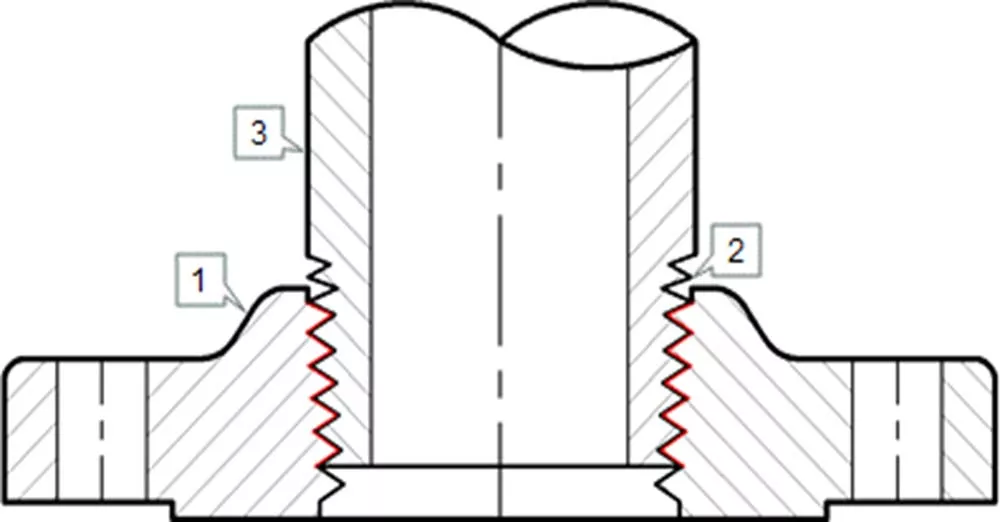 Threaded flanges are joined to pipes by screwing the pipe (which has a male thread, generally NPT per ASME B1.20.1) onto the flange, without seam welds (in certain cases, though, small welds are applied to increase the strength of the connection). Threaded flanges are available in sizes up to 4 inches and multiple pressure ratings, however, they are used, mostly, small size piping in low pressure and low-temperature applications, like water and air utility services. Threaded flanges are also a mandatory requirement in explosive areas, such as gas stations and plants, as the execution of welded connections in such environments would be dangerous.
Threaded flanges are joined to pipes by screwing the pipe (which has a male thread, generally NPT per ASME B1.20.1) onto the flange, without seam welds (in certain cases, though, small welds are applied to increase the strength of the connection). Threaded flanges are available in sizes up to 4 inches and multiple pressure ratings, however, they are used, mostly, small size piping in low pressure and low-temperature applications, like water and air utility services. Threaded flanges are also a mandatory requirement in explosive areas, such as gas stations and plants, as the execution of welded connections in such environments would be dangerous.
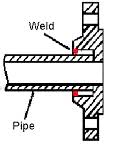
SOCKET WELD FLANGE
 .
. 
LAP JOINT FLANGE

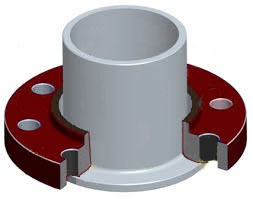
Lap joint flanges feature a flat face and are always used in conjunction with a stub end. Lap joint flanges resemble, in shape, slip-on flanges except for the radius at the crossing of the flange face and the bore to accommodate the flanged portion of the stub end. A lap joint flange slips over the pipe and seats on the back of the stub end and the two are kept together by the pressure of the bolts. The use of lap joint flanges in combination with stub ends is a cost-effective solution for stainless steel or nickel alloy pipelines, as the material of the lap joint flange can be of a lower grade (generally carbon steel) than the material of the stub end (which has to match the pipe grade, as in contact with the conveyed fluid). This arrangement, therefore, has these two advantages:
- reduces the overall cost of the pipeline’s flanged joints, as the use of higher grade materials is minimized;
- bolting operations are simplified, as the lap joint flange can be rotated around the pipe to help with bolts alignment.
BLIND FLANGE
 Contrary to all the flange types seen above, blind flanges do not have a center hole, and are used to blind or seal a pipeline, a valve/pressure vessel and block the flow of the fluid. Blind flanges have to withstand remarkable mechanical stress due to the system pressure and the required bolting forces. Blind flanges allow easy access to the pipeline, as they can be easily unbolted to let the operator execute activities inside the terminal end of the pipe (this is also the reason why the blind flange type is used as manhole for pressure vessels, at times). It is maybe interesting to observe that, while this flanges type is easier to manufacture, they are sold at a premium average cost per kilogram compared to the other flange types.
Contrary to all the flange types seen above, blind flanges do not have a center hole, and are used to blind or seal a pipeline, a valve/pressure vessel and block the flow of the fluid. Blind flanges have to withstand remarkable mechanical stress due to the system pressure and the required bolting forces. Blind flanges allow easy access to the pipeline, as they can be easily unbolted to let the operator execute activities inside the terminal end of the pipe (this is also the reason why the blind flange type is used as manhole for pressure vessels, at times). It is maybe interesting to observe that, while this flanges type is easier to manufacture, they are sold at a premium average cost per kilogram compared to the other flange types.
SPECIAL TYPES OF FLANGES
NIPOFLANGE

A Nipoflange is used for branch pipelines at 90 degrees and is a product manufactured by combining a welding neck flange with a forged Nipolet. However, a Nipoflange is a solid single piece of forged steel and not two different products welded together. To install a Nipoflange, the piping staff has to weld the Nipolet part of the device on the run pipe and bolt the flanged part on the flange of the branched pipe. Nipoflanges are available in different materials, such as carbon steel ASTM A105 (high-temperature service), ASTM A350 (low-temperature carbon steel), ASTM A182 (stainless steel grades, including duplex and super duplex) and nickel alloys (Inconel, Incoloy, Hastelloy, etc). Nipoflanges are also manufactured in the reinforced variant, which has additional mechanical strength compared to a standard Nipoflange.
WELDOFLANGE

A Weldoflange is conceptually similar to a Nipoflange, as that they are a combination of a weld neck flange and a branch fitting connection (a Weldolet in this case). Weldoflanges are made out of a single piece of solid forged steel, not by welding separate parts together.
ELBOFLANGE AND LATROFLANGE
Other less common types of flange Olets is the so-called Elboflange (a combination of a flange and an Elbolet) and “Latroflange” (combination of a flange with a Latrolet). Elboflanges are used to branch a pipeline at 45 degrees.

SWIVEL FLANGE
Swivel ring flanges facilitate the alignment of the bolt holes between the two mating flanges, a feature that is helpful in many circumstances, such as the installation of large diameter pipelines, subsea and offshore pipelines, pipe works in shallow waters and similar environments.Swivel flanges suit oil, gas, hydrocarbons, water, chemical and other demanding fluids in petrochemical and water management applications.
In the case of a large diameter pipeline, for instance, the pipe is fitted, at one end, with a standard welding neck flange, and with a swivel flange at the other end: by simply rotating the swivel flange on the pipe, the operators can achieve a perfect alignment of the bolt holes in a way easier and faster way.
The major standards for swivel ring flanges are ASME/ANSI, DIN, BS, EN, ISO, etc. The most common standard for petrochemical application is the ANSI/ASME B16.5 or ASME B16.47.

Swivel flanges are available in all the standard shapes of common flanges, i.e. weld-neck, slip-on, lap-joint, socket weld etc, in all material grades and in a wide dimensional range (sizes can vary from 3/8” to 60” and pressure rating from 150 to 2500). Swivel flanges can be manufactured in carbon steel (ASTM A105), alloy steel (ASTM A182 F1, A182 F5, A182 F9, A182 F91), and, stainless steel (ASTM A182 F304, A182 F304L, A182 F316, A182 F316L).
EXPANDING FLANGE (“EXPANDER”)

Expanding flanges, or “expander flanges”, are used to increase the bore of the pipeline from a specific point to another or to connect pipes to other mechanical devices such as pumps, compressors, and valves that have different inlets sizes. The expanding flange represented in the picture is a welding neck flange with a larger bore on the non-flanged end. Expanding flanges can be used to increase the run pipe bore only by one or maximum two sizes and not more (example: from 2 to 3 or maximum 4 inches). Expander flanges are a cheaper (and lighter) solution compared to the combination of a buttweld reducer and a standard flange (which is the standard solution for pipe bore increases above 2 sizes). The most common materials for expanding flanges are A105 (high-temp. carbon steel), A350 (LTCS) and ASTM A182 (stainless steel and above). Pressure ratings and dimensions of expanding flanges are in accordance with the ANSI/ASME B16.5 specification and are available with raised or flat face (RF, FF). 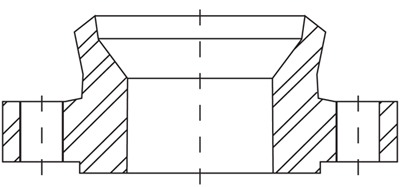 The drawing of an ASME expanding flange.
The drawing of an ASME expanding flange.
REDUCING FLANGE (“REDUCER”)

Reducing flanges, otherwise called reducer flanges, have an opposite function than expander flanges seen above, i.e. they are used to decrease the bore of a pipeline. The bore of the run pipe can be safely reduced by only 1 or 2 sizes (otherwise a solution based on the combination of a butt weld reducer and a standard flange has to be used). Reducing flanges are available in most sizes and material grades, and are not generally available from stock. Reducing flanges follow the same considerations in terms of specifications, sizes and material grades as expander flanges.
The last type of forged product that resembles the shape of a flange is the so-called spectacle blind: while not properly a flange, a blind (or a ring spacer or spade) is used in between pipes to isolate the pipeline mechanically and in a very easy way. More details are provided in another section of our Wiki for piping.
OTHER FLANGE CLASSIFICATIONS
The shape is the most obvious way to classify the different types of flanges. However, other ways to classify flanges exist and they are:
- by material grade
- by flange face type (raised, flat, ring joint, male and female, tongue and groove, lap joint)
- by flange finish (smooth, serrated, stock)
- by dimensions (nominal size and pressure rating)
Types of pipe fittings in oil and gas industry
M.E.G.A. designs, manufactures and supplies pipe fittings for the gas and oil industry, designed to last, providing safety special and standard products in a sensitive and important sector. The top 5 aspects of oil and gas are:
- The geological setting;
- Exploration and development;
- The production of new technology and fields;
- Decommissioning projects;
- The operating environment.
Our products are stable and reliable, certified according to current international standards. M.E.G.A. takes care of the whole process: from the design of pipe fittings to the actual construction and maintenance. As a reliable partner, we offer innovative polyolefin solutions for safer and more durable oil pipe fittings to help our customers meet the challenges of exploration, construction and supply. Do you need a consultation to understand better which product is more suitable for you?
Standard fittings for oil and gas industry
Standard oil pipe fittings and unions are high-quality products that reflect the needs of industries working in the extraction, refining, and gathering of petroleum products. Threaded or socket fittings are available in the variants: threaded, BW, flat and eccentric. This family of standard products for oil and gas industry are available in carbon steel, stainless steel, duplex and superduplex stainless steel, nickel alloys, copper alloys, titanium and others. The material can be NSF 61, NACE, PED and Norsok certified. 
Oil pressure pipe fittings
We have a wide range of products for oil&gas sector including oil pressure pipe fittings, accessories and adapters for all kinds of needs. Our company offers a wide range of low and high pressure pipe fittings for oil&gas and naval industries, pressure washers and earthmoving machines. Applications: Suitable for passing mineral oils, ASTM 3 type hydraulic oils, gasoline. Chemical resistance to brake oil (DOT type 4). Branch outlet fittings M.E.G.A. manufactures high-performance oil outlet fittings, capturing the customer’s specific needs and flexibly handling the entire production cycle of each branch fitting, starting from raw material sourcing and production, to the final testing stage and any inherent certification. For the oil and gas industry, megalets, self-reinforced shunts with a traditional 90° conformation to the main pipeline, stand out among other products. Depending on the different configurations, they are divided into:
- Latromegalet that can be installed to obtain a branch with an angle other than 90°
- Elbowmegalet that can be mounted on a bend.
- Insert megalet which can be welded directly inside the main pipe.
All these types can be supplied with butt-welded (BW), socket-welded, threaded, and even flanged ends. megalets have several advantages:
- Less filler material;
- Fewer welding hours;
- Greater controllability with CND.
Special oil pipe fittings
Among the special products for the oil and gas industry are:
- Fittings;
- Nozzles;
- Special Flanges.
All these special products are designed to meet the specific needs of the client: here the design is done from scratch, with an initial consultative phase up to the product prototype and final approval. Special oil pipe fittings are designed according to the customer guidance or to the requirements of international codes, including ASME B31.1, B31.3, B31.4, B31.8, ASME B&PV Code Section I, Section III, Section VIII Division 1 and Division 2, PED, RCC-M, EN 13480, EN 10253 or others. Among these fittings we have:
- Special tees;
- Special wyes;
- Special caps;
- Special flanges;
- Flanged fittings;
- Others.
Nozzles for oil and gas are manufactured to withstand fatigue, high pressure, and corrosion. They come in different configurations: flanged, non-flanged, transitional and inclined. Special flanges are manufactured according to the ASME B16.5, B16.47, API 6A, and ASME B&PV Section VIII Division 1 and Division 2 standards. Flanges are non-standard and produced according to specific customer requirements, such as welding neck and long welding neck flanges, misalignment flanges, swivel flanges, anchor flanges, orifice flanges, and blind flanges. 
Seamless pipes for oil and gas plants
Seamless oil pipe fittings are produced without welding. These products are used in different production points in the oil and gas industry: upstream operations, midstream operations such as transportation and distribution of different fluids including corrosive fluids. They are also used in downstream operations such as process piping for oil and gas refining in secondary products. The types of oil and gas seamless pipe fittings are produced in different materials:
- Seamless carbon steel pipes;
- Seamless stainless steel pipe fittings in ASTM A312 series;
- Seamless pipes in chromium-molybdenum alloy steel in grades such as ASTM A335 P5 to P91 for high temperature and pressure applications;
- Duplex and superduplex stainless steel pipe fittings;
Each pipe can be plated with CRA material (typically UNS N06625 or 316L) to ensure corrosion resistance.
Uses of welded pipe fittings in the oil and gas industry
Eventually, M.E.G.A. can manufacture welded pipe fittings for the oil and gas industry thanks to its internal welding team. We designed spools and other special assemblies to meet customer requirements with certified welds guaranteed by our quality system.
High-quality materials
As a worldwide supplier of oil pipe fittings, M.E.G.A. stands as a benchmark for the market due to its market knowledge and extensive experience in the sector. We have gained the trust of our customers through our philosophy, which includes:
- Completely in-house product realization, from raw material to finished product. Our entire supply chain is in-house;
- Certifications following the law (see next paragraph);
- Specific availability and expertise of our teams to rapidly solve any request or problem.
Our certifications comply with oil and gas standards
As a supplier to the oil and gas industry, we have achieved high-quality standards, certified by accredited bodies in the oil and gas industry. For organizations active in the oil and gas industry, certification to the relevant standard provides an important opportunity for standardization and improvement. Certification provides a system for continuous improvement of processes and products. Quality is sustainably assured and can be externally documented. Waste is reduced and the consequences of functional errors that may be caused by products and services are limited. In the chart below you will find all our certifications.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.